Understanding how to prove insurance bad faith can improve your chances of winning compensation for losses caused by the unscrupulous acts of your insurance company. Proving bad faith requires extensive investigation and preparation. If you suspect an insurance company is acting in bad faith, you need to build a record showing you attempted to resolve the matter. You also need evidence demonstrating the insurance company’s actions were arbitrary and capricious. You will need to gather all available documents regarding the claim, and your communication with the insurance company. Specifically, you need to gather the documents regarding your claim, and the insurance company’s denial of the claim. You also need to gather documents and information regarding why the insurance company denied the claim. If the insurance company denies your claim, appealing the denial and making a complaint to the Nevada Division of Insurance can help you build a strong case.
What Is Bad Faith Insurance?
Nevada defines bad faith insurance as “an actual or implied awareness of the absence of a reasonable basis for denying benefits of the policy”. To understand acts of bad faith, you will need to understand good faith insurance practices. Insurance companies are legally required to act fairly with all parties. Specifically, insurance companies must act fairly and honestly throughout all stages of claims, i.e., investigation, negotiation, and defense and/or settlement. Good faith includes providing coverage and defending the policyholder, settling a claim when it is apparent the claim should be settled and paying the claim in a reasonable amount of time.
Bad faith insurance practices can happen to various parties of a claim, i.e., the policyholder and any third parties who are seeking benefits. For example, a car accident victim may be the victim of bad faith if an insurance company wrongfully denies his or her claim. Similarly, the driver of the vehicle that caused the collision may be a victim of bad faith if the insurance company refuses to provide insurance coverage and a legal defense for the accident.
What Are the Elements of Bad Faith Insurance?
Bad faith insurance has two legal elements under Nevada law. An insurance carrier commits bad faith when they (1) deny benefits to the holder of the insurance policy, and (2) knew, or should have known, that there was no reasonable basis to deny the claim. A careful review of the facts of your case by an insurance dispute lawyer is often necessary to evaluate whether an insurance company’s actions qualify as bad faith. If your case is valid, your lawyer will guide you through how to file a bad faith insurance claim.
You have to prove three elements to win your case if you sue the insurance company. (1) First, you have to prove your claim was a covered loss. (2) Second, you have to prove the insurance company was obligated to honor the claim pursuant to the insurance policy. (3) Finally, you have to prove the insurance company acted in bad faith.
The Top Four Signs of a Bad Faith Insurer
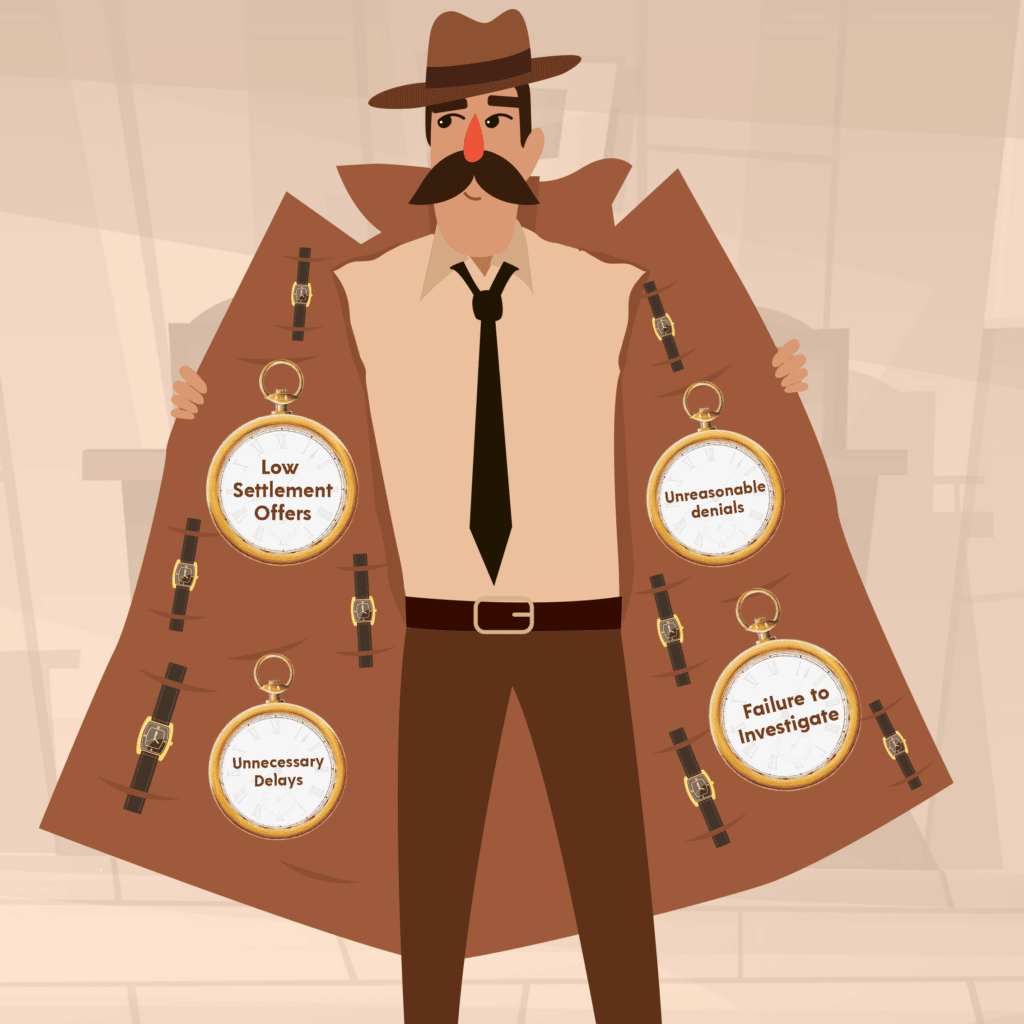


It is sometimes difficult to identify a bad faith insurer from an insurance company that is acting in good faith. In many cases, attempts to resolve insurance claims often reveal bad faith practices by insurance companies. The top four signs of a bad faith insurer include:
- Low Settlement Offers – Insurance companies are driven by profit. As such, it is not uncommon for insurance companies to make offers that people perceive as too low. This practice may cross into bad faith if an insurance company makes a low settlement offer before fully investigating the claim. This indicates the insurance company is motivated by profit as opposed to honoring its contractual obligation.
- Unnecessary Delays – Nevada State law imposes a variety of time requirements on insurance companies with regard to receiving, investigating, and paying claims. Bad faith insurers often delay claims or payments to see if the claimant gives up and abandons the claim.
- Unreasonable denials – Insurance companies are not permitted to arbitrarily deny claims. If an insurance company denies a claim, they must provide a valid reason.
- Failure to Investigate – Insurance companies investigate claims for a variety of reasons, e.g., to determine coverage, to obtain information regarding the claim and liability, and to learn the full extent of the loss to determine financial liability. Properly investigating a claim may require time and money. Accordingly, an insurance company may be acting in bad faith if they fail to investigate or fail to fully investigate a claim.
Other Examples of Bad Faith
There are many other signs an insurance carrier is acting in bad faith. These range from minor, e.g., failing to communicate with the insured, to more serious signs such as repeatedly requesting the same information and documents when investigating a claim. Another prominent example of bad faith is failing to defend the insured or failing to provide insurance coverage. This leaves the insured party at the mercy of the person making the claim. A related issue with the denial of coverage is the insurance carrier’s reason for denying coverage. Insurance companies sometimes deny coverage by making false or misleading statements regarding the insurance policy or misrepresenting the language of the insurance policy. Insurance companies sometimes threaten their policyholders or the person making the insurance claim. Finally, another common example of bad faith is when an insurance carrier delays paying out a claim.
Why Do Instances of Bad Faith Insurance Occur?
People and businesses purchase insurance as security in the event they suffer a loss or experience a traumatic incident. In exchange for paying a premium, an insurance carrier is required to provide coverage and benefits to the person or business they insure. Unfortunately, sometimes insurance carriers refuse to fulfill their contractual obligations and instead deny valid claims. Insurance carriers often do this because honoring a valid claim and providing coverage will require them to spend large sums of money. In some cases, insurance companies deny claims in bad faith with the hope that claimants simply give up.
Financial Compensation Available From a Bad Faith Insurance Claim
When an insurance carrier engages in bad faith conduct, it has a variety of effects. Insurance companies have a duty to defend the people and businesses they insure for any claims that are made against them and that are covered by the insurance policy. This duty to defend includes providing a legal defense. Victims of bad faith insurance often suffer extensive financial losses. This is because they have to handle the claim personally. For example, a victim may have to investigate and defend the claim, which means the victim is paying his or her own legal fees. If a judgment is obtained against a victim, they will personally have to satisfy the judgment or settlement.
Nevada law allows a victim to claim his or her actual losses. This includes a victim’s expenses, legal fees, and the cost of paying a judgment or settlement. Finally, Nevada law allows a victim to claim punitive damages. Unlike compensatory damages, which are designed to compensate a victim for his or her losses, punitive damages are designed to punish a wrongdoer and deter other potential wrongdoers. Nevada places caps on punitive damages. The cap is three times the amount of the victim’s actual losses. However, the cap for punitive damages is specifically waived for bad faith insurance claims. This is because of the egregious nature of bad faith insurance.